2:Global environmental change and geohazards
Climate change and other changes to the atmosphere, land use changes and soil degradation, freshwater depletion and contamination, and biodiversity loss are four important categories of “global environmental change.” These global environmental changes are due to increased human pressure on the environment, of which the main drivers are population growth and an increase in per capita resource use and waste production (Machenbach, 2007).
Geohazards may include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, coastal erosion, sea level rise, droughts, wildfires, typhoons, cyclones, huricanes, storms, floods, landslides, rising temperatures. These hazards are not only naturally induced but may be induced by anthropogenic causes.
Causes and consequences of the above phenomena are all important research subjects of JpGU scientists and researchers. We are trying to increase our efforts to openly present, publish and communicate our findings through our annual meetings, symposia, and scientific journals or social media and other opportunities.
 https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-announces-summer-2023-hottest-on-record/
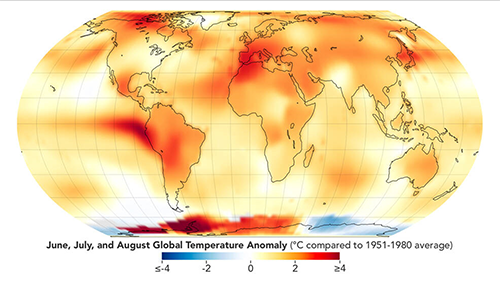
https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-announces-summer-2023-hottest-on-record/This map depicts global temperature anomalies for meteorological summer in 2023 (June, July, and August). It shows how much warmer or cooler different regions of Earth were compared to the baseline average from 1951 to 1980.
Credits: NASA Earth Observatory/Lauren Dauphin
